Air Source Heat Pumps take ambient warmth from outside and deliver it to the home, usually through warmed water that is circulated through the house in pipes and radiators, or underfloor heating. Let’s take a look at air source heat pump temperature in more detail.
Air Source Heat Pumps are usually able to generate heating temperatures of up to 65C. They are usually more efficient at temperatures within the range of 35-45C. High-Temperature air source heat pumps are capable of reaching temperatures of 80C, and could also reach 120C if needed.
The heating capabilities of this system make them suitable for heating homes efficiently while reducing carbon emissions. There are situations whereby the heat pump may struggle due to extreme weather conditions, which we would be looking into below.
How Does an Air Source Heat Pump Work?
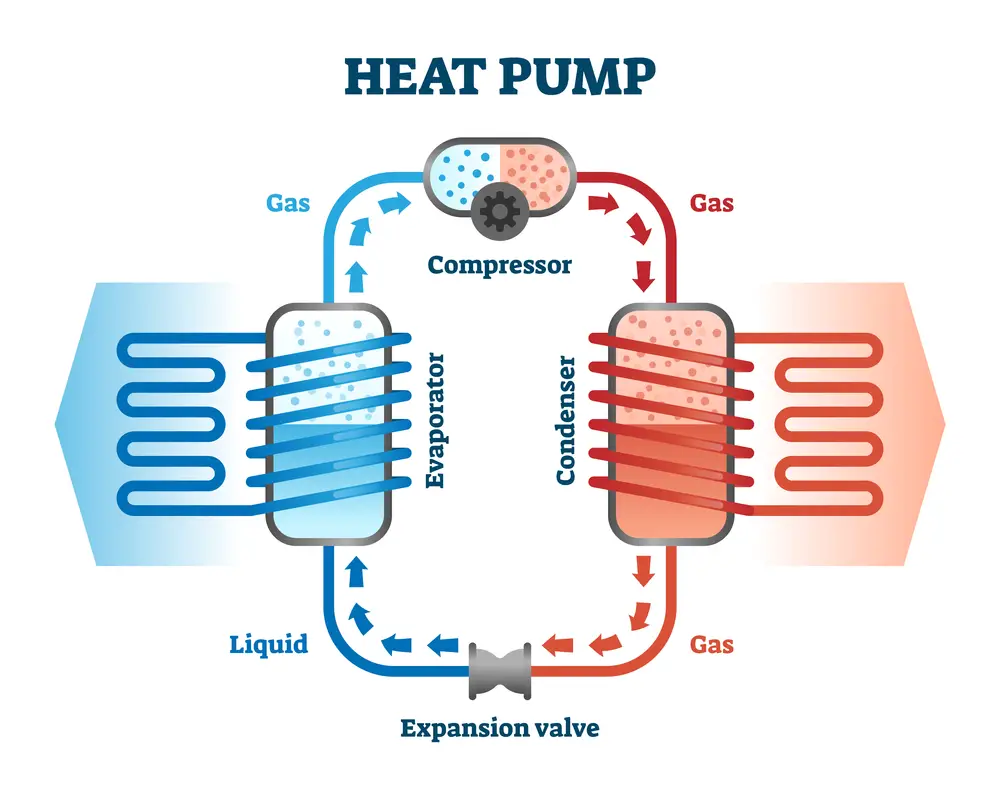
First, let’s see how an air source heat pump works. The outdoor unit takes heat from the outside air. The heat is absorbed by a liquid refrigerant. Then the system compresses the liquid refrigerant—a process that raises the temperature of the liquid. The heat absorbed by the liquid is sent to an underfloor heating system, radiator, or both.
When cooling is required, an air source heat pump works in reverse and therefore works a bit like a refrigerator. The flow of refrigerant is reversed, and the condenser coils and evaporator switch roles.
The refrigerant, which has a lower temperature than the indoor air, absorbs heat from the indoor air. The refrigerant is then put through the compressor, which heats the liquid and turns it into a gas. The heat is then transferred to the outside air via the condenser coils. The refrigerant then turns liquid again, cools down to below the room temperature, and the cycle is repeated.
Air source heat pumps can provide cooling too. In this process, the process described above is essentially reversed. Check out this dedicated article all about heat pump cooling.
What are the factors that affect Air Source Heat Pump Temperatures?
Air Source Heat Pumps have steady operating temperatures under working conditions. Although their temperatures could be affected by certain conditions which could lower the efficiency of the system. These factors include the following:
- Climate: This plays a major role in the efficiency of this system. Since the heat generated for this system is gotten from ambient air temperature, fluctuations in air temperature reduce the efficiency of this system. Most air source heat pumps would continue to function at most low temperatures, but with less efficiency.
As the temperature approaches -20C, the heat pump struggles to extract heat from ambient air and consequently fails to produce a steady supply of heat. At this point, it would be best to switch to the auxiliary heating system.
- Level of Insulation: The heat produced from this system could be lost to the environment if the home is not properly insulated. Before installing this system, the installer should ensure there is adequate insulation in the home and the heat outlet (underfloor heating). This is to prevent the heat pump from overworking while trying to overcome the heat losses in the system.
- Size of the Heat Pump: Improper sizing of the heat pump would lead to cold zones across the home when the heat pump is in operation. This is because the heat pump cannot efficiently generate enough heat for the room. This is usually common when radiators are used as the heating outlet.
- Heating System Components: The heating outlet(underfloor heating, radiators), and compressors all contribute to the efficiency of the system.
Check out our dedicated article about air source heat pumps and older houses here, where we delve into topics like insulation and pipework in more detail.
Is Hotter Better with Air Source Heat Pumps?
Before installing the air source heat pump, the heating medium for transferring heat has to be put under consideration. There are two major mediums for transferring heat generated from air source heat pump, they include the following:
- Air-to-Air Medium: The heat generated from the heat pump is transferred into the home through radiators. These radiators transfer heat across the room by releasing the heat directly into the air. This medium is considered inefficient and could be expensive since radiators do not distribute heat evenly.
To ensure the heat is dissipated evenly, it would require the use of large radiators, which would incur more running costs. Also, radiators require higher temperatures for heating, which adds to the heating costs.
- Air-to-Water medium: This medium entails the use of water running in pipes installed under the floor. This underfloor system efficiently dissipates heat evenly across the room. This is because underfloor heating requires low flow rate temperatures for heating, usually not more than 30C, hence low running costs.
Does turning the Air Source Heat Pump on and off affect temperature?
When underfloor heating is installed with air source heat pumps, the system would need to be kept on always. This is because it takes a considerable amount of time to get to favorable heating temperatures. Although keeping them on always would lead to an increase in heating cost since they have a slightly lower efficiency than ground source heat pumps.
An alternative to keeping it on constantly would be to pair it with a smart thermostat that can conveniently switch on and off when the temperature falls below or rises above certain thresholds.
When radiators are paired with air source heat pumps, they should only be switched on when needed. This is because they can heat up faster, unlike underfloor heating systems. Radiators consume more power since they require higher heating temperatures. Leaving them on would only lead to higher heating bills.
Check out our dedicated article that examines whether it is more efficient to leave an air source heat pump running for long periods of time compared to operating frequent on and off cycles.

What Temperature is Too Cold for an Air Source Heat Pump?
Air source heat pumps function effectively even at air temperatures of –15C. At this temperature, the efficiency reduces, but it is still able to supply heat effectively around the home. Air source heat pumps begin to struggle to provide adequate heat at temperatures below this point. At this point, it could be best to switch off the heat pump since it can no longer provide adequate heat.
This is to prevent a situation that would cause the heat pump from damaging itself. At this point, the backup system should be running since the heat pumps can no longer function effectively. Air source heat pumps should be able to provide adequate heating and cooling all year round, except in Polar Regions. This is due to the severity of their climate conditions.
Do Air Source Heat Pumps work in Below Freezing Temperatures?
On average, air-source heat pumps have a Coefficient of Performance of 3.2, under normal working conditions. As the temperature tends toward below freezing, the COP begins to decline as well. At this point, the heat pump consumes the same amount of energy it produces or even less, leading to a sharp decrease in efficiency until it can no longer produce substantial heat.

High-Temperature Air Source Heat Pumps
These types of air-source heat pumps are used to achieve high temperatures when compared to conventional ones. These heat pumps can attain temperatures of up to 80C and could get to 120C if required. This is a result of the cascaded refrigerant system built in them.
This type of heat pump was designed to replace conventional boilers since they do the same job with lower running costs and are eco-friendly. In comparison, High-temperature heat pumps will require more power than conventional heat pumps. This makes them less efficient since they would incur more running costs than conventional heat pumps.
When installing high-temperature heat pumps, it would be of note that they won’t be too compatible with underfloor heating systems. This is because the system may struggle to regulate the temperature needed for the underfloor system and to boil water. The temperature difference across both outlets also makes them less efficient systems.
These high-temperature heat pumps are more suitable for radiators since they require high flow rate temperatures for operation. Kindly go through Purethermal heat pumps for more information regarding their product specifications. Other manufacturers such as Daikin and LG’s heat pumps can reach temperatures of 65 and 80C respectively.
Low-Temperature Heat Pumps vs High-Temperature Heat pumps
The differences between these types of heat pumps are as follows:
| Low-Temperature Heat Pumps | High-Temperature Heat Pumps |
| They are more compatible with underfloor heating. | They are more compatible with radiators. |
| They cannot be efficiently used to replace boilers. | High-temperature heat pumps were designed to replace boilers. |
| These systems have a maximum temperature of 55C. | This heat pump can achieve temperatures of up to 80C and could even get to 120C if needed. |
| These systems are more efficient and have lower running costs. | High-Temperature heat pumps are less efficient and have higher running costs. |
| The cost of the installation here is low. | High cost of installation. |
Air Source Heat Pump Temperature Summary
Air source heat pumps have specific temperature ranges at which they function effectively. This is usually between 35 and 45C, even for high-temperature air source heat pumps. The lower the temperature of heat required from the heat pump, the greater the efficiency and vice versa.
High-Temperature heat pumps were designed to replace heat pumps while having better efficiency. These systems are not as efficient as low-temperature heat pumps and have no carbon emissions compared to boilers. Since they can achieve high temperatures, they can be used for boiling water conveniently.
Certain factors such as extreme weather conditions, the level of insulation in the property, and the size of the heat pumps affect the expected temperature of the system. Underfloor heating systems are more efficient and should be paired with smart thermostats to have a substantial amount of heat always. Radiators should only be turned on when needed since they heat up faster.
