In recent years, air-source heat pumps have emerged as a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional central heating systems. Air source heat pumps have their pros and cons, which must be put into consideration before installing them, as it renders them not suitable for every property.
Air Source heat pumps are durable alternative heating and cooling systems that boast good environmental credentials and are usually cheaper than a conventional boiler. They are energy-efficient although could be noisy while working. They are less energy efficient in harsh weather conditions.
| Pros | Cons |
| Energy efficient | The heat pump unit is noisy |
| Costs less to run than a conventional fossil fuel-burning system | Less efficient in extremely cold weather |
| Environmentally friendly | High Cost of installation, when compared to conventional boilers. |
| The installation process is easy | Requires space for outdoor unit. |
| Compatible with underfloor heating systems and radiators | Requires a substantial amount of insulation in the property to be properly efficient. |
| Remarkably durable(can last up to 20-25 years), while requiring little maintenance | |
| Likely to be eligible for renewable energy grants | |
| Can be used for cooling and heating |
This article focuses on the pros and cons of air source heat pumps. Learn about the nuances of the technology so that you can make an informed decision.
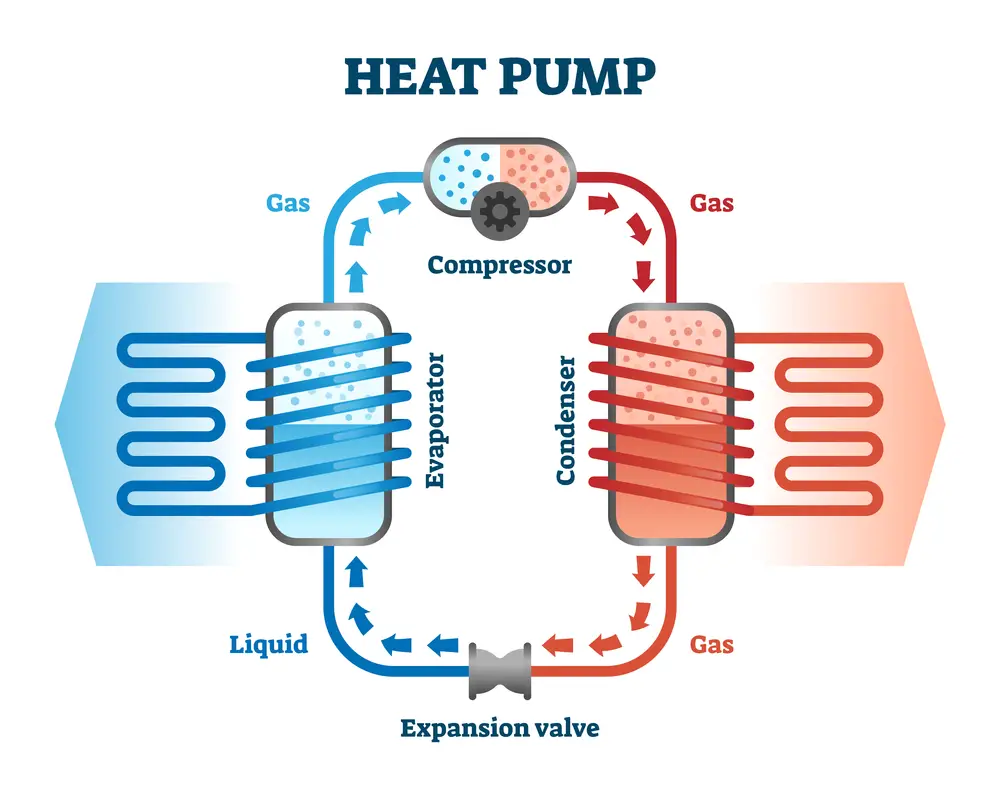
How Does an Air Source Heat Pump Work?
First, let’s see how an air source heat pump works. The outdoor unit takes heat from the outside air. The heat is absorbed by a liquid refrigerant. Then the system compresses the liquid refrigerant—a process that raises the temperature of the liquid. The heat absorbed by the liquid is sent to an underfloor heating system, radiator, or both.
When cooling is required, an air source heat pump works in reverse and therefore works a bit like a refrigerator. The flow of refrigerant is reversed, and the condenser coils and evaporator switch roles.
The refrigerant, which has a lower temperature than the indoor air, absorbs heat from the indoor air. The refrigerant is then put through the compressor, which heats the liquid and turns it into a gas. The heat is then transferred to the outside air via the condenser coils. The refrigerant then turns liquid again, cools down to below the room temperature, and the cycle is repeated.
When it comes to providing cooling with an air source heat pump, using underfloor heating or radiators is not a very good idea. They work pretty well when they are used for providing heat, but for cooling, there is a better option—chilled beams.
A chilled beam is a type of radiation system used to provide cooling. Pipes of water are passed through a beam, which is essentially a heat exchanger. The beam is attached to the ceiling of a room. Warmer air rises to the chilled beam. As the air comes in contact with the beam, the air cools down, condenses, and then falls downward.
Hot air rises and cool air falls downward, and this principle explains why a chilled beam is a good option for providing cooling with a heat pump.
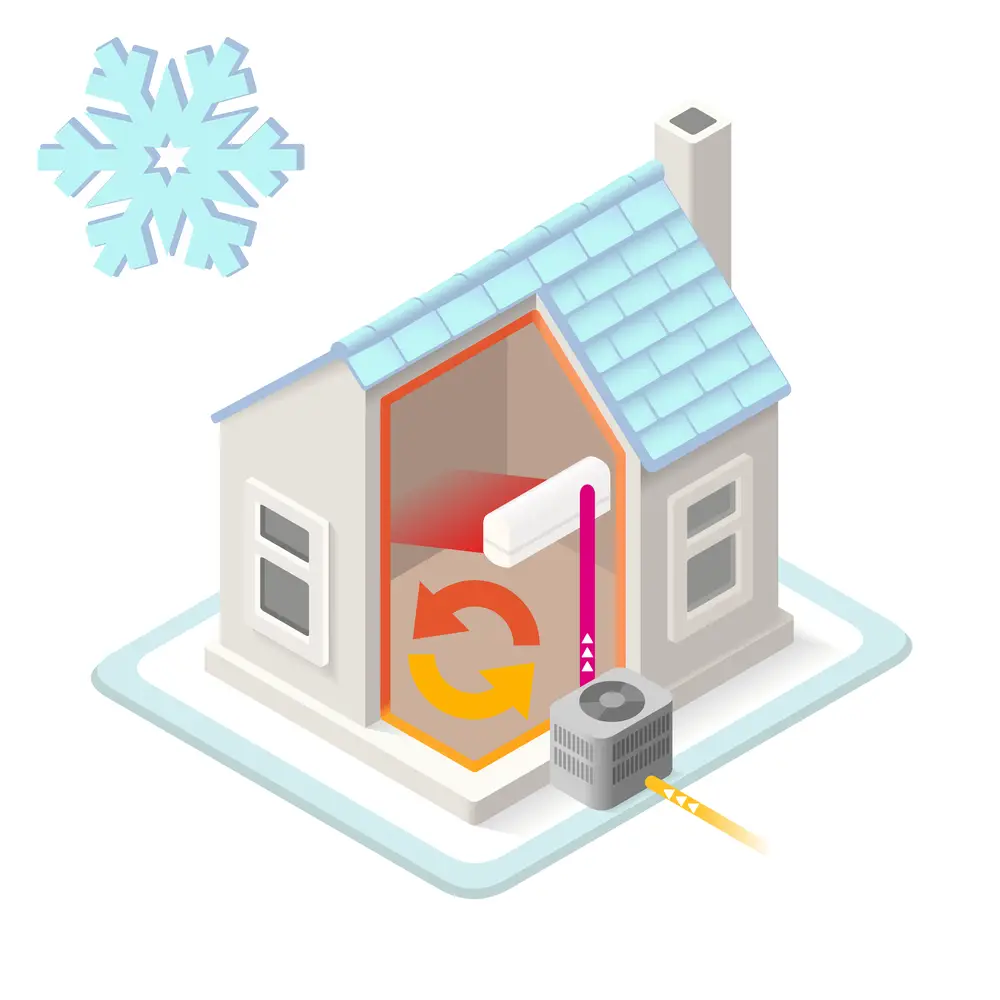

Pros of Air Source Heat Pumps
Energy-Efficient
An air-source heat pump is a two-in-one system that provides both heating and cooling. When the outside temperature is around 7°C, the system runs at a COP of 3.2. That means, that for each unit of energy used to extract heat from the air, the system is capable of producing 3.2 units of heat energy.
This efficiency may vary to some extent depending on factors such as the temperature in the outside air and the level of insulation your home has. A 12,000 BTU heat pump with a COP of 3 uses roughly 4,000 kWh of electricity per year.
Check out our dedicated article all about the energy use and efficiency of air source heat pumps here.
Low Carbon Footprint
An air-source heat pump can reduce carbon emissions by more than 23 tonnes over a decade. The system emits up to 20% less CO2 than a gas boiler, and about 70% less than an electric heating system. This is why so many people interested in reducing their carbon footprint are showing interest in air source and ground source heat pumps.
Both Heating and Cooling
One of the most remarkable advantages of an ASHP is that the system can be used for heating in the cold months and cooling in summer. The system can extract heat from ambient air even when temperatures drop to −30 °C, although performance drops when temperatures go below 0°C.
This two-in-one system can keep your home comfortable year-round. The pump is paired with an underfloor heating system, which can be left running non-stop during the winter. In the summer, the same system provides cooling. If you get a smart thermostat installed, you will not even have to set temperatures. Depending on the outside temperatures, the thermostat will automatically set temperature levels.
Check out this dedicated article about heat pump cooling here.
Easy Installation
While it’s not a DIY project, the installation of an air source heat pump can be professionally done in just a day or two. Installing an ASHP does not require digging loops, and that’s part of the reason the process is easier than installing a ground source heat pump.
In most places, no planning permissions are required for installing an air source heat pump. In general, the process is quick and easy. You just have to find a reliable technician.
Low Maintenance
An air-source heat pump is a low maintenance system, in part because it has fewer moving parts than a traditional boiler. To ensure optimal performance of the system, just get it serviced once a year. Maintenance involves unclogging fan blades, filters and coils, checking refrigerant levels, and checking for leaks.
While the heat pump does not require frequent servicing and maintenance, regular maintenance prolongs the lifespan of the system.
Works in Cold Climates
Surprisingly, an air source heat pump can extract heat from the air even when temperatures drop to as low as -10°C for conventional heat pumps and -30°C for cascaded heat pumps. The system loses its efficiency to some extent as temperatures drop, but cutting-edge ASHPs that use newer technologies can provide heating in extremely cold regions. The newer models are remarkably more sophisticated and powerful than the older ones.

Long Lifespan
Air source heat pumps are remarkably long-lasting. With proper maintenance, a pump can smoothly run for 20-25 years. Better yet, most ASHPs come with 5-year warranties. It is to be noted here that the durability of a heat pump largely depends on its price. The ones on the expensive side are longer lasting and require less maintenance.
Given the fact that the lifespan of a traditional boiler is only 12-15 years, an ASHP is worth investing in. The main reason an ASHP lasts longer than a traditional boiler is that the former has fewer moving parts.
Can Be Used to Heat Swimming Pools
Using an air source heat pump is a low-carbon and efficient way to heat a swimming pool. You can use a dedicated swimming pool heat pump or attach a suitably sized heat exchanger to your domestic heat pump for the purpose. ASHPs especially designed to heat swimming pools come with heat exchangers made of titanium, which remains unaffected by the chemicals in pool waters.
No Fuel Storage
An air-source heat pump does not rely on oil or gas and therefore does not need fuel storage. The system uses electricity to run. You don’t need extra space for fuel storage, and you don’t have to pay fees for fuel deliveries. These pumps look minimalistic and are ideal for small properties.
Safe
ASHPs are safe mainly because they don’t burn fossil fuel to generate heat. There is no risk of carbon monoxide leaks. In a monoblock system, the refrigerant is sealed and placed outside the home. Air source heat pumps and ground source heat pumps are among the safest types of heating systems, according to Energy Saving Trust.
A water leak is the worst thing that can happen to an ASHP, and the issue can be addressed pretty easily. A leaking heat pump could signify bad or dirty air filters, low level of refrigerants, or a blocked air duct. You can visit here for more information on the implication of a leaking heat pump.

Air Source Heat Pumps are Compatible with Both Underfloor Heating and Radiators
Air source heat pumps are usually paired with underfloor heating systems, but they also work pretty well with traditional radiators and smart radiators. Many homeowners use underfloor heating downstairs and radiators upstairs. ASHPs are low-temperature systems and therefore should be paired with radiators with large surface areas.
Cons of Air Source Heat Pumps
With all the amazing advantages, air-source heat pumps have some disadvantages as well. To get the most out of the system, you have to get underfloor heating installed and make sure your home is well-insulated. Here are the problems associated with air-source heat pumps:
High Upfront Costs
The total cost for a ductless central air source heat pump will be somewhere between $10,500 and $18,975. The cost depends on the number of indoor air handler units you need. For each indoor air handling unit, the price will be $3,500-$5,200.
As we have stated, ASHPs should be paired with underfloor heating systems. Unless you already have an underfloor heating system installed, you have to be prepared to invest in one.
Low Heat Supply
An ASHP does not provide the same level of heat as a conventional oil or gas boiler. Due to its low heat supply, an ASHP requires a heat emitter with a large surface, such as an underfloor heating system. If you want to use standard radiators that operate at high temperatures, a traditional oil or gas boiler is a better option than an air source heat pump.
Noise
An air-source heat pump makes some noise, like an air conditioning unit. If you are sensitive to noise, you may find it annoying. However, by being a little bit strategic, you can resolve the noise issue.
Just place the unit far from the quiet zones of your home. Newer models make a lot less noise than older ones. Therefore, if you invest in a cutting-edge air source heat pump, you may not have to deal with the issue of noise.
Low Efficiency in Cold Weather
An air-source heat pump can indeed operate even when temperatures drop to -30°C, but the system becomes less efficient as temperatures go below 0°C. In other words, the efficiency of the system largely depends on the outside air.
To avoid this problem, many people living in extremely cold regions opt for ground source heat pumps. They extract heat from the ground, which is a stable source of heat. The underground temperature doesn’t fluctuate, and as a result, you get a steady supply of heat, no matter how cold the outside temperature is.
May Not Be Compatible with Your Existing Radiators
These pumps work with radiators with large surface areas. That’s why your existing radiators are not likely to be compatible with an ASHP. It is intended to work in conjunction with an underfloor heating system. But if you are not yet ready to get an underfloor heating system installed, you will have to buy large radiators.

High Levels of Insulation Needed
Air source heat pumps operate at low temperatures, around 35°C to 45°C. This is why these heat pumps are paired with underfloor heating systems. Unless your home has a high level of insulation, an ASHP may not meet the heating requirements of your home.
The efficiency of the system largely depends on how well-insulated your home is. In general, homes that were built before the 1970s have low levels of insulation.
Check out our dedicated article all about air source heat pumps in old houses, coming soon!
A Supplementary Heating Source May Be Needed
In the depths of winter(below −10 °C), an air source heat pump may not be enough to keep your home comfortably warm, especially if your home is not well-insulated. In such a case, you will have to invest in a supplemental heating source, such as a traditional boiler. Homeowners living in very cold regions prefer hybrid heat pumps.
Conclusion – Is it really worth it?
We have discussed the pros and cons of air source heat pumps, and we hope you have found the information useful. The advantages of air source heat pumps make them a very viable option for heating homes, especially when considering their impact on the environment.
| Pros | Cons |
| Energy efficient | The heat pump unit is noisy |
| Costs less to run than a conventional fossil fuel-burning system | Struggles in extremely cold weather |
| Environmentally friendly | High Cost of installation, when compared to conventional boilers. |
| The installation process is easy | Requires space for outdoor unit. |
| Compatible with underfloor heating systems and radiators | Requires a substantial amount of insulation in the property to be properly efficient. |
| Remarkably durable(can last up to 20-25 years), while requiring little maintenance | |
| Likely to be eligible for renewable energy grants | |
| Can be used for cooling and heating |
Air source heat pumps qualify for Renewable Heat Incentives, as a means of enticing more people into adopting these heat pumps.
Air source heat pumps tend to struggle in extreme cold weather conditions. Extensive research should be carried out about the weather conditions in that vicinity. This is to ensure the heat pump is suitable for that area or to provide a supplementary heating system if the heat pump would be insufficient.
We hope now you have a pretty good understanding of the benefits and drawbacks of air source heat pumps and are ready to make an informed decision. To make things easier, contact a reliable provider who can walk you through the whole process.