When installing air source heat pumps, one must evaluate the environmental pros and cons. Air source heat pumps utilise the sun’s energy but are also run from mains electricity. Lets discover whether air source heat pumps are environmentally friendly.
Air source heat pumps do not produce any carbon waste, other than needing mains energy to run the pump. They are efficient and use the sun’s energy to heat your home. They do produce some noise. In comparison to other heating systems, air source heat pumps are environmentally friendly.
| Environmental Advantages | Environmental Disadvantages |
| Use of renewable energy (solar warming of the earth) | Noise Pollution. |
| Year-round warming availability | |
| No carbon emissions (barring mains energy use to run the heat pump) | |
| Highly efficient (see below) |
A well-installed air source heat pump system presents many benefits that help to maintain a green, comfortable, and healthy environment. The rest of this article will explain in detail the impact of this system on the environment.
How do Air Source Heat Pumps work?
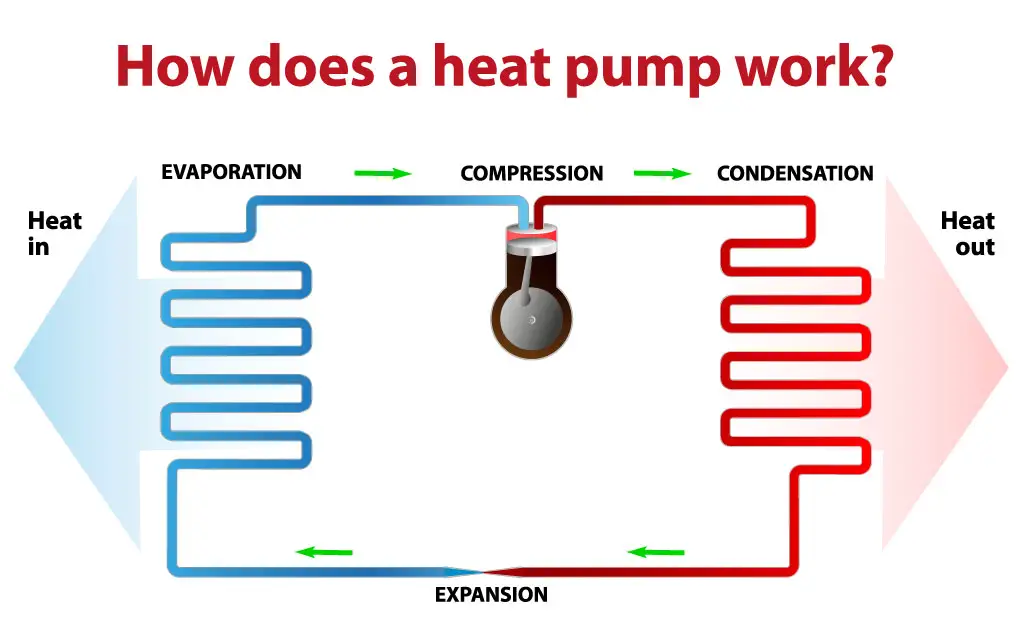
First, let’s see how an air source heat pump works. The outdoor unit takes heat from the outside air. The heat is absorbed by a liquid refrigerant. Then the system compresses the liquid refrigerant—a process that raises the temperature of the liquid. The heat absorbed by the liquid is sent to an underfloor heating system, radiator, or both.
When cooling is required, an air source heat pump works in reverse and therefore works a bit like a refrigerator. The flow of refrigerant is reversed, and the condenser coils and evaporator switch roles.
The refrigerant, which has a lower temperature than the indoor air, absorbs heat from the indoor air. The refrigerant is then put through the compressor, which heats the liquid and turns it into a gas. The heat is then transferred to the outside air via the condenser coils. The refrigerant then turns liquid again, cools down to below the room temperature, and the cycle is repeated.
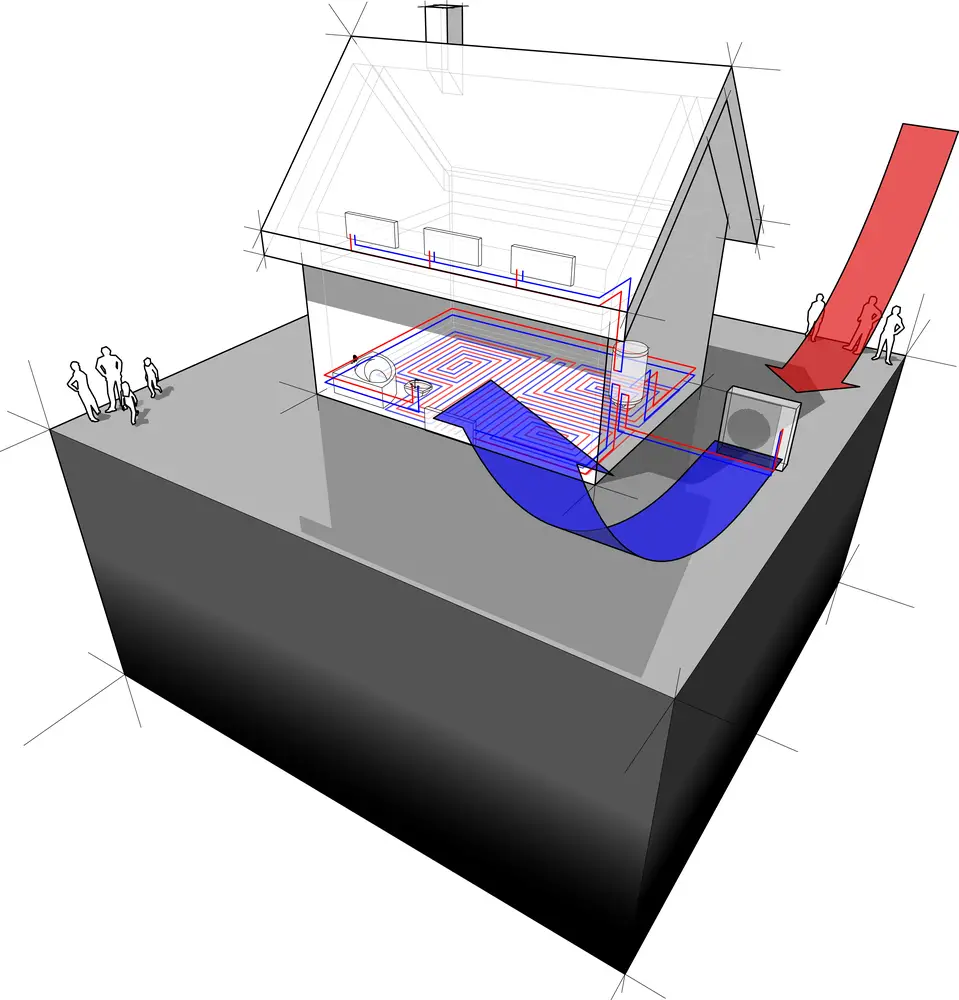
What is the impact on the local environment when an Air source heat pump is installed?
Unlike ground source heat pumps, an Air source heat pump poses a not-so-severe detrimental implication on the environment. It only raises eyebrows due to the noise which emanates from them when in operation. The noise they generate is usually between 40-60dB which could be disturbing for the neighbors, especially during peak hours of operation.
Due to this noise, it is best installed far from the windows of the property or far away from the neighbor’s property. If this cannot be achieved, an acoustic enclosure could be used. This dampens the sound and vibrations from the heat pump.
Air source heat pumps are not as destructive as ground source heat pumps when they are being installed. Air source heat pumps only require ample space where the outdoor unit would be situated and where the indoor unit would also be mounted.

How efficient are air source heat pump systems?
A modern air source heat pump system can achieve an efficiency of up to 320% but could fluctuate due to air temperatures. In other words, if your air source heat pump has this level of efficiency, it can deliver over 3 units of cooling/heating (CoP of 3.2) from 1 unit of electricity.
The efficiency of this system begins to fluctuate as air temperatures reach subzero temperatures. Depending on the quality of the heat pump system you have installed, a heat pump can operate efficiently at a lower temperature. Usually, the temperature at which the unit is no longer able to extract heat efficiently falls between –15 and -22 degrees Celsius.
The efficiency of a ground source heat pump is based on its CoP (Coefficient of performance). The higher the CoP of the heat pump, the lower the amount of input energy it will need to run.
Potential Advantages of Air Source Heat Pumps on the Environment
The benefits of Air source heat pumps include the following:
Low Carbon Footprint
An air-source heat pump can reduce carbon emissions by more than 23 tonnes over a decade. The system emits up to 20% less CO2 than a gas boiler, and about 70% less than an electric heating system. This is why so many people interested in reducing their carbon footprint are showing interest in air source and ground source heat pumps.
The figure below compares the benefits of running a heat pump versus other fossil fuel technologies as the National Grid gradually achieves a low carbon emission program. The blue, yellow, and green lines represent the amount of CO2 produced by various electricity-generating methods. The green indicates the current level of pollution from renewable sources alone (Wind and Solar) of 0.3 kg CO2/kWh, which will decrease as the CoP rises.
CO2 emissions from power generation are currently predicted to be 0.422 (kg CO2/kWh) in the United Kingdom. This is usually higher in the winter when demand for energy for heating is at its highest in coal-fired power plants. This figure is lower during the night when load demand is lowest and the producing station switches to nuclear energy as a source of energy.
Kindly visit renewableenergyhub.co.uk for more information.
Energy-Efficient
An air-source heat pump is a two-in-one system that provides both heating and cooling. When the outside temperature is around 7°C, the system runs at a COP of 3.2. That means, that for each unit of energy used to extract heat from the air, the system is capable of producing 3.2 units of heat energy.
This efficiency may vary to some extent depending on factors such as the temperature in the outside air and the level of insulation your home has. A 12,000 BTU (British thermal units) heat pump with a COP of 3 uses roughly 4,000 kWh of electricity per year.
Check out our dedicated article all about the energy use and efficiency of air source heat pumps here.
Environmental Effect of Refrigerants on the Environment
Because of their involvement in global warming, several governments have banned various forms of refrigerants. Hydrochlorofluorocarbons, such as R22, R404, R12, and even hydrocarbons like R290, make up the majority of these refrigerants. Hydrofluorocarbons like R410A and R32 are being employed in these heat pumps because they have little to no impact on the ozone layer in the event of a leak or after their service life.
Air source heat pumps with R410A are also gradually being phased out since the refrigerant still contributes (very little) to the ozone layer depletion. R32 on the other hand is now the recommended refrigerant for heat pumps. This is because it causes no harm to the ozone layer when a leak occurs.
Can Air Source heat pumps be considered renewable energy?
In general terms, air-source heat pumps can be considered renewable energy because the energy that these pumps rely on is inexhaustible. If you could run the pump from electricity derived from a renewable energy source, then the system becomes carbon-neutral too.

How much heat can be generated by an air source heat pump, how much warmth will this provide through the floors?
A system of underfloor heating circulates 40-45°C water across the floor area to heat the entire house. In comparison, a traditional radiator system requires much hotter water, around 70-80°C, to heat the room/s with a much smaller surface area. Therefore, combining an air source heat pump with underfloor heating is the best way to get the maximum benefit from your heat pump system.
Air source heat pumps usually operate at maximum efficiency when the outside air temperature is around 7°C. At this air temperature, they can deliver a flow temperature of 35°C to the heating systems of your house. The flow temperature is the temperature of the water being delivered to your underfloor heating system and other heating solutions at home from the ASHP.
Running costs of Air Source Heat Pumps
The two factors affecting the cost of operating an air source heat pump are highly interrelated:
- Heat requirement: Each property has a different heat demand, which describes how much heating power is required to maintain the correct temperature.
- Heat demand: The air source heat pump’s efficiency is determined by how much electricity it uses when it is heating a property
A heat pump can produce 3 kWh of heat from 1 kWh of electricity. In the case of an annual heating demand of 9,000 kWh, 3,000 kWh of electricity will be needed. With 3,000 kWh of electricity priced at £0.16 a unit in the UK, annual heating costs will be around £480. You can visit Besthomeheating.com for more information.
Grants for Air Source Heat Pumps
The just-concluded grant for heat pumps(Renewable Heat Incentive) has been upgraded to the Boiler Upgrade Scheme for homeowners. This scheme would run from April 2022 to April 2025.
The government’s Boiler Upgrade Scheme (BUS) aims to minimize our carbon emissions. It’s for homes and companies in England and Wales that want to switch from fossil fuel or electric heating to a renewable system like air or ground source pumps, or even biomass.
Here, homes that apply for this scheme are eligible for a £5000 benefit for any expenses related to the air source heat pump. Visit Edfenergy for more information on heat pump grants.
Conclusion – Main Environmental Considerations when installing Air source heat pumps
Installing an air source heat pump has fewer drawbacks than installing a ground source heat pump. The noise produced by this system is the biggest turnoff about them. It may be overlooked in some cases. Air source heat pumps offer similar benefits to ground source heat pumps, but at a lower efficiency.
Air source heat pumps provide a safe, healthy, and environmentally friendly working environment. They do not produce their own carbon emissions. They are not entirely “green” because they rely on electricity that could be obtained from fossil sources. To avoid carbon emissions, the device could be combined with a renewable energy source.
The required permits must be obtained before the installation of this system. This is to avoid possible sanctions following installation. Air source heat pumps are a potential option for ground source heat pumps in regions where land is limited.
Check out all our other information on air source heat pumps here:
- What temperatures do air source heat pumps produce?
- Will air source heat pumps work in an old house?
- Air Source Heat Pump Pros and Cons
- Should air source heat pumps ever be turned off?
- Can air source heat pumps be combined with radiators?
- How efficient are air source heat pumps? Costs and Efficiency explained
- Can you combine air source heat pumps with underfloor heating?
- How long do heat pumps last? Air Source Heat Pump Lifespans
- Are air source heat pumps safe?
- Are air source heat pumps environmentally friendly?
